What Is the Difference Between SASE and VPN?
The distinction between SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) and VPN (Virtual Private Network) has become a key topic in modern networking. Both technologies aim to enhance network security, but they differ significantly in their architecture, use cases, and how they protect data.
1. Core Purpose
- VPN: A VPN creates a secure connection between a user’s device and a remote network by encrypting the internet traffic. It is primarily designed to extend the reach of a private network to remote users or devices.
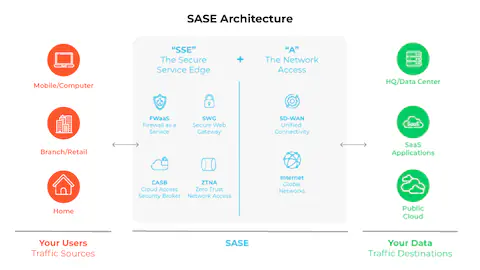
- SASE: SASE combines network security services (like secure web gateways, firewall-as-a-service, and CASB) with WAN capabilities in a unified cloud-native platform. Its core purpose is to provide secure access to any device, from anywhere, while ensuring consistent policy enforcement.
2. Architecture
- VPN: Traditional VPNs are typically hardware-based or use on-premises software to create a secure tunnel. They are often deployed on a specific perimeter network, which can limit scalability and flexibility.
- SASE: SASE is a cloud-based framework that integrates multiple security and networking services into one unified platform. It provides a decentralized approach, meaning security is applied at the edge of the network (closer to the user) rather than at a centralized data center.
3. Security Focus
- VPN: While VPNs offer encryption, they don’t inherently provide robust security features like threat detection, data loss prevention, or real-time security monitoring. Their focus is mainly on creating a secure tunnel for data transfer.
- SASE: SASE offers a comprehensive security model, integrating multiple services such as CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker), SWG (Secure Web Gateway), firewall-as-a-service, and ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access). It is designed to secure users and devices wherever they are located, regardless of whether they are on the corporate network or accessing public resources.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
- VPN: Scaling VPNs can be difficult and expensive, especially for large enterprises with multiple remote users. VPNs may require additional hardware or software as traffic increases or new users are added.
- SASE: SASE is built to scale effortlessly. Since it’s cloud-based, it can adapt to growing businesses by automatically extending security and networking capabilities without the need for significant on-premises infrastructure upgrades.
5. User Experience
- VPN: VPNs can sometimes cause latency and slow down performance, especially if users are connecting to distant servers. The centralized nature of VPN networks can also lead to bottlenecks in traffic.
- SASE: With SASE, users get better performance because the service is cloud-based and operates closer to the end user. It optimizes network performance and reduces latency by routing traffic through the nearest edge location, ensuring fast, reliable access to applications.
6. Cost Considerations
- VPN: The cost of VPN solutions can be relatively lower initially, but as your business grows, you may need to invest in additional infrastructure and management tools, which can make it less cost-effective for large-scale operations.
- SASE: While SASE may require a higher initial investment, its subscription-based model and integrated services can be more cost-efficient in the long run. The centralized cloud architecture reduces the need for multiple security tools and services, offering a consolidated cost structure.
Conclusion
The decision between SASE and VPN ultimately depends on the specific needs of your organization. VPN is a tried-and-true solution for secure, remote connections, particularly for smaller or more traditional setups. However, SASE is the future-forward solution for modern enterprises that require a flexible, scalable, and highly secure network architecture that supports the needs of a distributed workforce.





Post Comment